

- WHAT COULD CAUSE BUZZING FROM AUDIO INTERFACE AND MIC PLUS
- WHAT COULD CAUSE BUZZING FROM AUDIO INTERFACE AND MIC FREE
The peak-level therefore always is higher than the RMS-level (unless the signal is a pure square-wave). The peak value and the RMS value of that signal are both indicated in the diagram.
WHAT COULD CAUSE BUZZING FROM AUDIO INTERFACE AND MIC PLUS
The peak value, however, is the portion of the waveform (on either side, plus or minus) that is the farthest away from the 0-line. This measure expresses a kind of average value based on the energy contained within the signal. When measuring the level of a signal, we often use RMS, which means Root Mean Square. However, above 1 kHz, the signal is boosted, especially in the ITU-curve methodology.

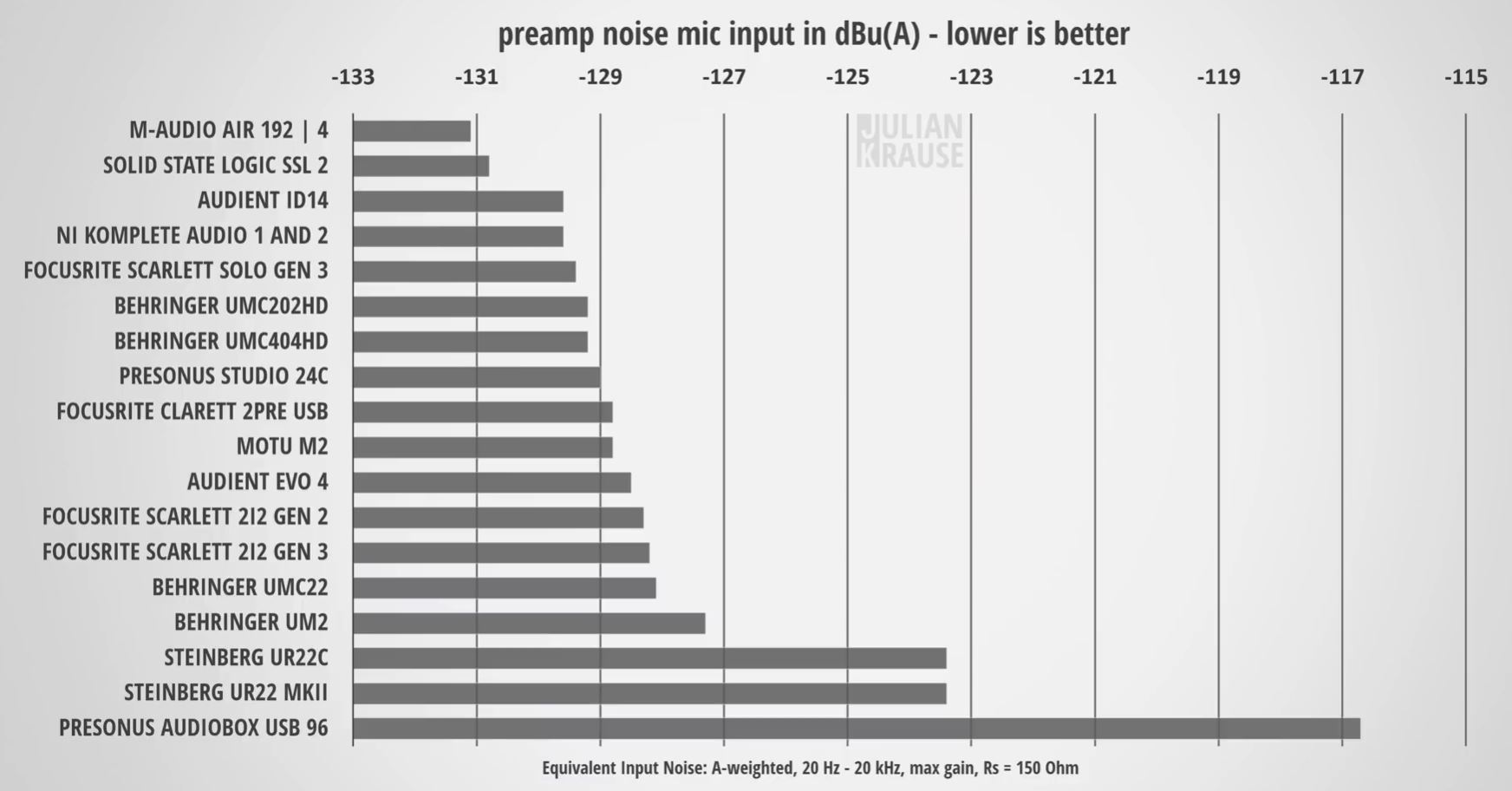
The weighting-curves reduce the signal at low frequencies. These curves are much alike, introduced to compensate for the frequency response of the ear at low levels. We use two different frequency-weighting curves: A-weighting and ITU-weighting (formerly also known as the CCIR-weighting). We will explore what the difference means. The numbers we get from each of these methods are different. The two methods are A-weighted, RMS and ITU-weighted, Quasi-peak. When we measure the noise of a microphone – and present the result in the spec sheet – we use two different methods as stated in the standards (IEC 60268-4 Microphones, Clause 16.2 Method of measurement). The noise is therefore equivalent to that of an external sound source. However, there is no sound source to produce the signal the microphone itself produces the 4-µV signal recorded. If the sensitivity is 20 mV/Pa, the output of that microphpone would be approximately 4 µV.
WHAT COULD CAUSE BUZZING FROM AUDIO INTERFACE AND MIC FREE
Now, if the microphone was completely free of noise we could record a sound source that had a SPL of 22 dB(A). Self-noise is the signal the microphone produces of itself, even when no sound source is present.Įxample: A microphone has an equivalent noise level of 22 dB(A).
Noise is expressed by the equivalent noise level. Sometimes it sounds darker, other times it sounds lighter – all depending on the type of microphone and its design. When we amplify it, we can hear that it sometimes sounds "smooth”, other times it sounds more "crackling”. However, the character of the noise may differ, depending on the distribution of the noise. We call it "noise" because there are no tones in the signal.

Just as white light contains the whole spectrum of visible light, white noise contains an equal amount of energy at all audio frequencies. The name "white noise" comes from comparing audio to light. The basic nature of the noise is what we call white noise. The movement of air molecules causes a bombardment on the diaphragm, which eventually ends up as noise. Also, thermal noise (or "Johnson noise") is an issue the higher temperature, the higher the noise.įurther, noise is generated due to the presence of air around the microphone. Primarily this noise originates from a current running in the circuitry (so-called "shot noise" or "Poisson noise"). However, there is always some portion of noise generated by the microphone itself – self-noise. Noise is not something we want to hear from a microphone. You will find data quantifying the "equivalent noise level”, which describes what goes on at the bottom of the microphone’s dynamic range – basically in the range of low SPLs. Unfortunately, completely free is impossible! To prepare for a good audio result, you should check the microphone's noise specifications. When we use a microphone, we expect the cleanest possible signal, ideally completely free of annoying noise.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
